Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that combines the flexibility of rubber with the processability of plastic. This method is essential in producing soft-touch, durable, and flexible products for various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices. In this article, we will explore the process of TPE injection molding, compare TPE with TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), discuss the manufacturers involved in this process, and examine the intricacies of TPE injection molds.
Understanding TPE Injection Molding
What is TPE?
TPE, or thermoplastic elastomer, is a class of copolymers that exhibit both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties. This means that TPE materials can be stretched and flexed like rubber while still being recyclable and processable like plastic. Due to this unique combination, TPE is used in a variety of applications, from automotive seals to medical tubing.
The TPE Injection Molding Process
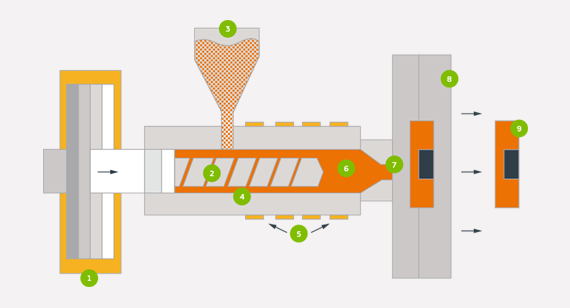
The injection molding process for TPE involves several steps:
- Material Selection – The appropriate grade of TPE is chosen based on the application.
- Melting and Injection – The TPE material is heated to a specific temperature and injected into a mold cavity under high pressure.
- Cooling and Solidification – The molten TPE cools down and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold.
- Ejection and Post-Processing – The finished product is ejected from the mold, followed by any necessary finishing processes like trimming or surface treatment.
This process ensures that TPE parts are produced with high precision and consistency, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
TPE vs. TPU Injection Molding: A Detailed Comparison
When considering thermoplastic elastomers for injection molding, another common material that often comes up is TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane). Both TPE and TPU have unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
Material Properties Comparison
| Property | TPE | TPU |
| Flexibility | Higher elasticity, softer feel | Less flexible but more rigid |
| Durability | Good for moderate wear applications | High wear resistance and toughness |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and abrasions |
| Processing Ease | Easier to process in injection molding | Requires precise processing conditions |
| Applications | Used in grips, seals, overmolded parts | Common in industrial parts, wheels, sports gear |
Which One Should You Choose?
- If your product requires a soft-touch, highly flexible, and cost-effective material, TPE is the better choice.
- If abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and toughness are primary concerns, TPU is the better option.
- TPE is generally more user-friendly for injection molding, while TPU demands strict processing controls.
By understanding the differences, manufacturers can select the best material based on the specific needs of their products.
TPE Injection Molding Manufacturers: Key Players in the Industry
Several manufacturers specialize in TPE injection molding, offering services ranging from custom mold designs to high-volume production. Here are some leading TPE injection molding manufacturers:
1. Kraiburg TPE
Kraiburg TPE is a global leader in TPE materials and custom injection molding. Their products cater to industries such as automotive, consumer goods, and healthcare.
2. RTP Company
RTP Company provides custom-engineered TPE materials, ensuring that manufacturers receive tailor-made solutions for their specific applications.
3. Teknor Apex
Teknor Apex is known for its broad range of thermoplastic elastomers, offering solutions for medical devices, automotive parts, and industrial components.
4. Avient Corporation
Formerly known as PolyOne, Avient Corporation specializes in TPE compounds and provides comprehensive injection molding services.
5. Star Thermoplastics
This manufacturer focuses on producing high-quality TPE materials for overmolding, seals, and grips.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
When selecting a TPE injection molding manufacturer, consider:
- Their experience with TPE-specific molding processes
- Their ability to provide custom formulations
- Their quality certifications, such as ISO 9001 or ISO 13485 (for medical applications)
- Their production capacity and ability to meet your volume requirements
By working with a reputable manufacturer, businesses can ensure high-quality and consistent production of TPE-based products.
TPE Injection Mold: Designing for Efficiency and Quality
Mold Design Considerations
The design of a TPE injection mold plays a crucial role in the success of the molding process. Some important considerations include:
- Mold Material – High-quality steel or aluminum molds are typically used for TPE molding.
- Gate Placement – Proper gate location ensures uniform material flow and prevents defects.
- Cooling System – Efficient cooling designs improve cycle time and part quality.
- Venting – Proper venting prevents air traps and ensures consistent part formation.
Common Issues in TPE Molding and Their Solutions
- Warping & Shrinkage – Optimizing cooling rates and mold design can reduce distortion.
- Short Shots – Ensuring proper injection pressure and temperature settings prevents incomplete filling.
- Flashing – Proper clamping force and mold design minimize excess material around edges.
By addressing these factors, manufacturers can enhance the quality of TPE-molded parts while improving production efficiency.
TPE injection molding is an essential process for producing flexible, durable, and high-performance components across multiple industries. By understanding the differences between TPE and TPU, selecting the right manufacturer, and optimizing mold design, businesses can achieve high-quality results in their injection molding projects.
With its versatility and cost-effectiveness, TPE continues to be a top choice for injection molding applications, making it a crucial material in modern manufacturing
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) injection molding has revolutionized the production of flexible, durable, and soft-touch plastic components across industries such as automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer goods. This method combines the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastic, enabling manufacturers to create high-quality parts with excellent material performance. This comprehensive guide will explore every aspect of TPE injection molding, including the molding process, a comparison between TPE and TPU, a detailed look at leading manufacturers, and an in-depth discussion on the design and function of TPE injection molds. We will also touch on important factors like sustainability, cost considerations, and innovations in TPE injection molding technology.
Understanding TPE Injection Molding in Detail
What Makes TPE Unique?
TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) is a category of materials that exhibit both thermoplastic and elastomeric characteristics. Unlike traditional rubber, TPE can be melted and reshaped multiple times, making it highly versatile and cost-effective for manufacturers. Some of its key properties include:
- High flexibility and softness – Ideal for grips, overmolded parts, and comfort-based applications.
- Recyclability – Unlike thermoset rubbers, TPE can be remelted and reused, reducing waste.
- Excellent weather and chemical resistance – Ensures durability in harsh environments.
- Good adhesion with other plastics – Suitable for overmolding applications with materials like ABS, PP, and PC.
These properties make TPE a preferred choice for a wide range of products, from medical tubing to automotive seals.
Step-by-Step TPE Injection Molding Process
- Material Preparation
- TPE pellets are dried to remove moisture, which can cause defects in the final part.
- The material is pre-mixed if color or additives are required.
- Injection and Molding
- The TPE material is fed into an injection molding machine, where it is heated to a molten state.
- The molten TPE is injected into a pre-designed mold cavity under high pressure.
- Cooling and Solidification
- The material cools and solidifies within the mold, taking its final shape.
- Efficient cooling systems help speed up production while maintaining quality.
- Ejection and Finishing
- The solidified part is ejected from the mold.
- Additional finishing processes, such as trimming excess material or surface texturing, may be applied.
TPE vs. TPU Injection Molding: Which One is Better?
TPE and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) are often compared due to their similar elastic properties. However, each material has distinct characteristics that affect its performance in injection molding applications.
Key Differences Between TPE and TPU
| Property | TPE | TPU |
| Elasticity | High flexibility, softer feel | Less flexible, more rigid |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High (ideal for applications requiring durability) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and solvents | Superior resistance to chemicals and abrasions |
| Overmolding Capability | Excellent for bonding with rigid plastics | Good but requires precise adhesion control |
| Processing Complexity | Easier to mold and process | Requires tighter control of temperature and pressure |
When to Choose TPE Over TPU
- If the application requires a soft, rubber-like feel (e.g., grips, comfort products).
- If cost-effectiveness and easy processing are priorities.
- If overmolding with rigid plastics is a major requirement.
On the other hand, TPU is ideal for applications demanding abrasion resistance, toughness, and long-term durability.
TPE Injection Molding Manufacturers: Who Are the Industry Leaders?
The demand for high-quality TPE components has led to the rise of specialized manufacturers who provide custom molding solutions. Here are some of the top TPE injection molding companies worldwide:
1. Kraiburg TPE
A global leader in thermoplastic elastomers, Kraiburg TPE supplies high-quality TPE compounds for automotive, medical, and industrial applications.
2. RTP Company
RTP Company specializes in custom-engineered thermoplastics, including TPE materials designed for specific performance requirements.
3. Teknor Apex
A major supplier of TPE materials, Teknor Apex offers solutions for medical devices, soft-touch grips, and industrial applications.
4. Avient Corporation
Formerly known as PolyOne, Avient Corporation provides a wide range of TPE formulations tailored to the automotive, electronics, and medical industries.
5. Star Thermoplastics
Star Thermoplastics is known for its expertise in producing soft-touch TPEs used in consumer goods, overmolded handles, and flexible seals.
Injection Mold China: A Major Manufacturing Hub
China is a leading global hub for TPE injection molding, with numerous manufacturers offering cost-effective solutions and large-scale production capabilities. Many companies source TPE molds and finished components from China due to the country’s advanced molding technologies, skilled workforce, and competitive pricing.
TPE Injection Mold Design: Key Factors for High-Quality Production
The efficiency and quality of TPE injection molding depend significantly on mold design. Poorly designed molds can lead to defects, production delays, and increased costs.
Important Mold Design Considerations
- Material Selection for the Mold
- High-quality steel molds ensure longevity and precision.
- Aluminum molds are used for prototypes or low-volume production.
- Gate Placement and Flow Control
- Proper gate design ensures uniform material flow and prevents defects like short shots or sink marks.
- Cooling System Efficiency
- A well-designed cooling system reduces cycle times and improves part consistency.
- Venting and Ejection System
- Adequate venting prevents air traps, while an optimized ejection system ensures smooth part release.
Common Defects and Solutions in TPE Molding
| Defect | Cause | Solution |
| Warping | Uneven cooling | Optimize cooling rate, adjust mold temperature |
| Flashing | Excess material leaking out | Improve clamping force, refine mold edges |
| Short Shots | Incomplete filling | Increase injection pressure, optimize gate design |
| Sink Marks | Uneven material thickness | Adjust mold temperature and cooling system |
Proper mold design is crucial for minimizing defects and ensuring efficient, high-quality production.
Sustainability and Cost Considerations in TPE Injection Molding
Eco-Friendly Aspects of TPE
One of the significant advantages of TPE over traditional rubber is its recyclability. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable TPE formulations that reduce environmental impact.
Cost Factors in TPE Injection Molding
Several factors influence the cost of TPE molding:
- Material Costs – TPE grades vary in price depending on their formulation and application.
- Mold Costs – High-precision molds require greater investment but improve efficiency in the long run.
- Production Volume – High-volume production lowers per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
- Labor and Machine Costs – Automated systems reduce labor costs and improve consistency.
By optimizing material selection, mold design, and production efficiency, businesses can reduce costs while maintaining high-quality output.
Challenges and Solutions in TPE Injection Molding
While TPE injection molding offers numerous advantages, it is not without its challenges. Manufacturers often encounter issues such as material inconsistencies, processing difficulties, and design limitations that can impact the final product’s quality and performance. Addressing these challenges requires a deep understanding of material science, mold design, and process optimization. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common challenges faced in TPE injection molding and explore effective solutions to overcome them.
1. Material Selection and Compatibility
One of the biggest challenges in TPE injection molding is selecting the right material for a specific application. TPEs come in various formulations, each with unique properties, such as hardness, elasticity, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Using an incorrect grade of TPE can lead to performance issues, such as insufficient flexibility, poor adhesion in overmolding applications, or degradation under certain environmental conditions.
Solution: To address this challenge, manufacturers should work closely with material suppliers to select the most suitable TPE formulation. Conducting material compatibility tests and prototype trials can help ensure that the chosen TPE meets the required specifications. Additionally, considering factors like operating temperature, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress can guide material selection.
2. Processing Challenges in Injection Molding
Processing TPE in an injection molding machine requires precise control of temperature, pressure, and cooling rates. Unlike rigid thermoplastics, TPEs are more sensitive to temperature variations, which can lead to defects such as short shots, warping, or sink marks. Additionally, TPEs have a lower viscosity compared to other plastics, making them prone to flashing, where excess material seeps out of the mold cavity.
Solution: To optimize processing, manufacturers should fine-tune injection parameters such as melt temperature, injection speed, and holding pressure. Proper mold design, including adequate venting and gate placement, can improve material flow and reduce defects. Using an injection molding machine with precise temperature and pressure control capabilities is also crucial for maintaining consistency in TPE molding.
3. Overmolding and Adhesion Issues
TPE is often used in overmolding applications, where it is molded over a rigid plastic substrate to create a soft-touch grip or a flexible seal. However, achieving strong adhesion between TPE and other plastics (such as ABS, PC, or PP) can be challenging, especially if the materials have poor compatibility. Weak adhesion can lead to product failure, delamination, or peeling over time.
Solution: The key to successful overmolding is selecting a TPE grade specifically designed for adhesion to the base material. Additionally, surface preparation techniques such as chemical primers, plasma treatment, or mechanical texturing can enhance bonding. Proper mold design, including optimized gate locations and controlled melt flow, can further improve adhesion and prevent defects.
4. Shrinkage and Warping
TPE parts can experience shrinkage or warping during the cooling process, leading to dimensional inaccuracies and poor fitment. These issues are particularly problematic in precision applications, such as automotive seals or medical devices, where tight tolerances are required.
Solution: Managing cooling rates is critical to preventing shrinkage and warping. A well-designed cooling system with uniform temperature distribution can help maintain part integrity. Additionally, using mold flow simulation software during the design phase allows manufacturers to predict shrinkage behavior and make necessary adjustments before production begins.
By understanding these challenges and implementing the right solutions, manufacturers can improve efficiency, reduce defects, and produce high-quality TPE injection molded products.
Future Trends and Innovations in TPE Injection Molding
- Advanced Overmolding Techniques – New bonding technologies improve TPE adhesion with rigid plastics.
- Biodegradable TPEs – The industry is shifting toward eco-friendly TPE alternatives.
- Smart Manufacturing (Industry 4.0) – AI and automation are improving process efficiency.
- 3D-Printed Molds for Prototyping – Rapid prototyping with 3D-printed molds is cutting development costs.
As technology advances, TPE injection molding will continue evolving, offering improved sustainability, efficiency, and product performance.
Conclusion
TPE injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that provides numerous advantages over traditional rubber and plastic materials. By understanding the molding process, selecting the right material (TPE vs. TPU), and choosing a reliable manufacturer, businesses can achieve high-quality, cost-effective, and sustainable production. With continuous advancements in mold design, material science, and manufacturing technology, TPE injection molding remains a critical process in the modern manufacturing industry.